3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing that uses technologies similar to standard inkjet printers, however in 3D. The technique of making anything in layers, adding material continually until the final design is complete, is referred to as additive manufacturing. This phrase is most commonly used to relate to moulding and 3D printing.
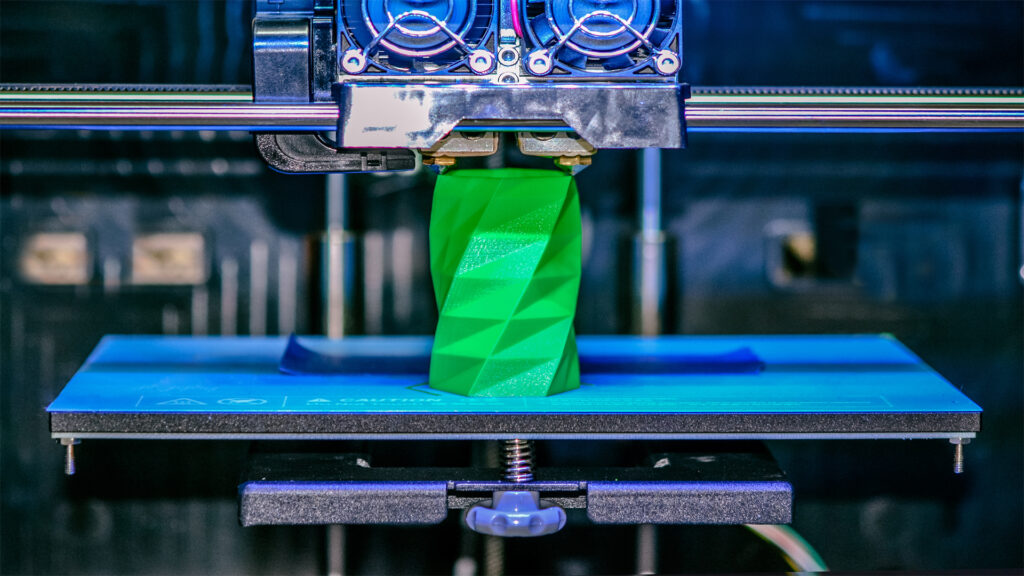

To manufacture a three-dimensional object from scratch, a mix of cutting-edge software, powder-like materials, and precision instruments is required.
Essential 3D Printing Supplies
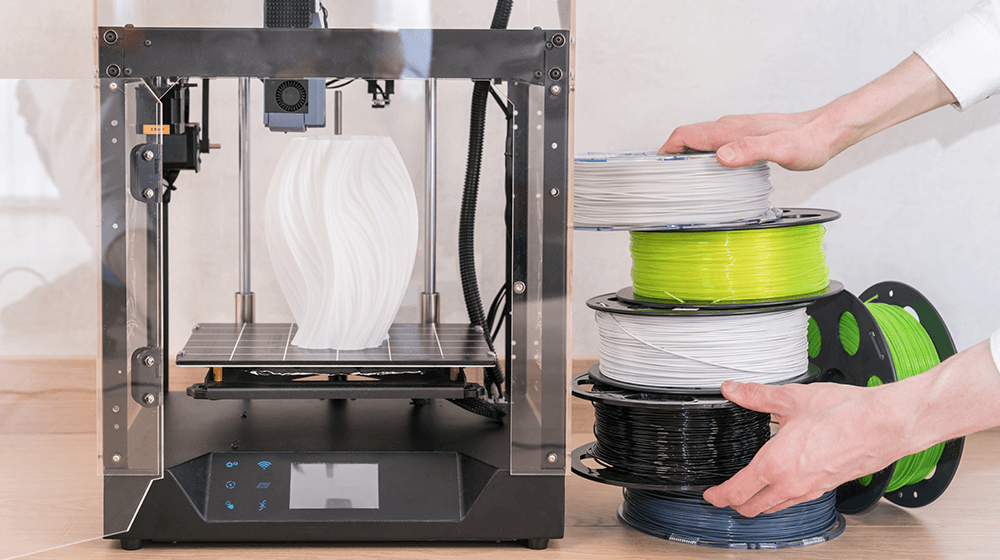
A printer employs a variety of materials to duplicate an object to the best of its ability. Here are a couple of such examples:
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) Filamets
ASA filament (acrylonitrile styrene acrylate) is the ideal all-purpose 3D printing thermoplastic for a wide range of uses. It is chemically comparable to ABS plastic but has three advantages: greater mechanical qualities, higher aesthetics, and UV resistance. Typical uses of the ASA filament available for purchase online include concept model prototyping, early prototyping, and functional prototypes. It is also utilised for low-volume manufacturing and highly customised items.
Carbon Fibre Filaments
Carbon fibre filaments are used to make products that must be both strong and lightweight.
Conductive Filaments
These printing materials are still in the testing stage, but they can be used to create electric circuits without the use of wires. This is a material that can be used in wearable technologies.
Flexible Filaments
Flexible filaments create prints that are both pliable and durable. These materials can be used to print on a variety of items ranging from wristwatches to phone covers.
Metal Filaments
Metal filaments are created by combining finely ground metals with polymer glue. To achieve the true look and feel of a metal object, it can be made of steel, brass, bronze, or copper.
Wooden Filaments
These filaments are made of finely ground wood powder and polymer glue. These are used to print wooden-looking things and might appear lighter or darker depending on the printer’s temperature.
It’s also important to note that the 3D printing process can take a few hours for very simple prints, such as a box or a ball, to days or weeks for much larger complicated projects, such as a full-sized house.
Different 3D Printing Methods and Techniques
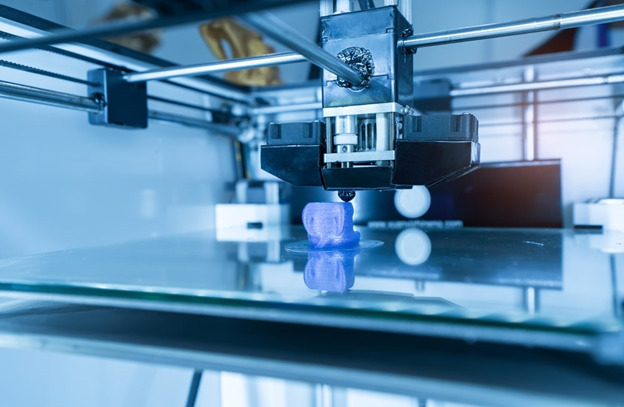

There are also various sorts of 3D printers available, depending on the size, detail, and scope of a project. The way an object is produced will vary slightly depending on the type of printer used.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling)
FDM is most likely the most popular type of 3D printing. It’s quite useful for making plastic prototypes and models.
SLA (Stereolithography) Technology
SLA is a type of rapid prototyping printing that is best suited for printing in fine detail. The printer creates the things in hours using an ultraviolet laser.
DLP (Digital Light Processing)
DLP is one of the most traditional types of 3D printing. Because the layers dry in seconds, DLP printing may generate prints at a faster rate than SLA printing.
CLIP (Continuous Liquid Interface Production)
CLIP is one of the quicker VAT photopolymerisation techniques. CLIP technology is used to project a succession of UV pictures across a cross-section of a 3D-printed item, resulting in a perfectly controlled curing process. After that, the part is baked in a thermal bath or oven, which causes multiple chemical processes that allow the part to solidify.
Material Jetting
This part allows for particles of material through a relatively small nozzle layer by layer to create a platform that is hardened by UV radiation.
Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting makes use of a powder base material that is evenly coated with a liquid binder that is delivered through jet nozzles to act as an adhesive for the powder particles.
Fused Deposition Modelling
Fused filament fabrication (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), works by unravelling a plastic thread from a spool and directing it through a heated nozzle in horizontal and vertical paths, producing the object as the molten material hardens.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS is a type of Powder Bed Fusion that employs a high-powered laser to fuse microscopic particles of powder to create a three-dimensional shape. The laser scans and selectively fuses each layer on a powder bed before lowering the powder bed by one thickness and repeating the process till completion.
MJF (Multi-Jet Fusion)
This is another type of Powder Bed Fusion that makes use of a sweeping arm to drop powder and an inkjet-equipped arm to selectively apply binder on top. The detailing agent is then applied precisely around the detailing agent. Finally, thermal energy is used to initiate a chemical reaction. This identical procedure is used in Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), but using metal powder.
Sheet Lamination
Sheet lamination uses external force to bind material in sheets and layered ultrasonic welding to join them. The sheets are then machined on a CNC machine to make the shape of the product.
DED (Directed Energy Deposition)
Directed Energy Deposition is a metal industrial technique that uses a 3D printing device attached to a multi-axis robotic arm with a nozzle for dispensing metal powder. The powder is applied to a surface and an energy source, which melts the substance and solidifies it.






















