Since their introduction, servo motors have proven themselves quite useful in many industries. For many years, servo motors have been involved in completion of big tasks. They might be small in size, but they are very powerful and energy efficient. With these features, servo motors are extensively used for operating remotely controlled toy cars, airplanes, robots and various industrial devices. Over the recent years, servo motors have been also used in industrial applications, in-line manufacturing plants, pharmaceutical services, robotics and food services.
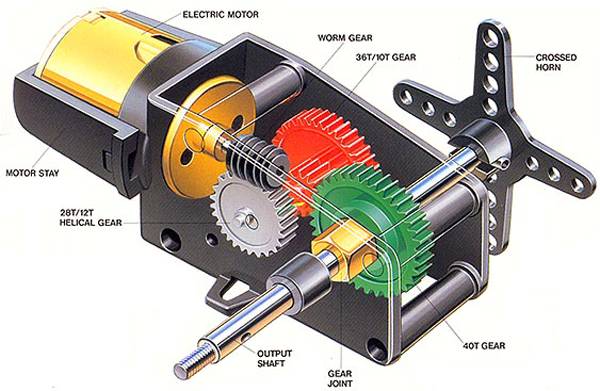
The working principle of servo motors is simple, yet highly efficient. The servo circuitry is built right inside the motor unit and it uses a flexible shaft, usually fitted with a gear. An electric signal controls the motor and it also determines the amount of movement of the shaft. The set up inside servo motors is simple: small DC motor, control circuit and potentiometer. The DC motor is attached to the control wheel via gears and as it rotates, the resistance of the potentiometer changes and the control circuit is able to accurately regulate the movement and its direction.
The power supply to the motor stops when the shaft is at the right (desired) position. If the shaft doesn’t stop at the desired position, the motor is running until it gets into the appropriate direction. The desired position is sent through the signal wire, which uses electrical pulses. So, the speed of the motor is proportional to the actual and desired position. When the motor is near the desired position, it starts turning slowly, but when far, it turns fast. In other words, servo motors run only as fast as necessary to complete the task, which makes them highly efficient devices.
In general, there are two types of servo motors: AC motors and DC motors. DC servo motors are ideal for smaller applications, but are not capable of handling high current surges. However, AC servo motors are able to deal with higher current surges and find a big use in industrial machinery. When it comes to price, DC motors are less expensive than AC servos, so they are used a lot more. Also, DC motors are especially designed for continuous rotation, which makes them perfect for robot movements.
With all their unique capabilities, servo motors can be used in many different applications. In radio-controlled airplanes, they are used to position control surfaces, such as robots, elevators, rudders, etc. In in-line manufacturing, servo motors are used as high repetition and accurate work is required.





















